Ligase Dna Replication Diagram | When you look at model or diagram of dna, and go about the task of replicating it, you can see the bases, think of the base to do this, a final enzyme, dna ligase (n), comes and closes the gap between fragments. Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as dna, is a nucleic acid that has three main components: How dna replication occurs in cells. Dna replication occurs through a semiconservative mechanism, because each new molecule is made up of one old strand and one new strand. At the completion of synthesis, dna ligase seals the breaks between the okazaki fragments as well as around the primers to form continuous strands.
Genetic information present in double stranded dna molecule is transmitted from one cell to another cell and to progeny by faithful replication of dna. Dna is the genetic material and is propagated throughout generations. Изображение dna ligase diagram replication. Schematic diagram of dna replication. This leads to the formation of two.

During dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. Dna is the genetic material and is propagated throughout generations. The majority of ligation reactions involve dna fragments that have been generated by restriction enzyme digestion. Mammalian cells contain four dna ligase isozymes. Short segment of dna synthesized discontinuously in small segments in the 3' to 5' direction by ligase. The rna primers are removed and replaced with dna nucleotides by bacterial dna polymerase i, and dna ligase seals the gaps between these fragments. The two copies of dna produced contain one original strand and one new strand. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell. The lagging strand is therefore synthesised in fragments. Dna replication — steps & diagram. Schematic diagram of dna replication. Prokaryotes replicate their dna in the cytoplasm. The fragments are then sealed together by an enzyme called ligase.
Dna replication occurs through a semiconservative mechanism, because each new molecule is made up of one old strand and one new strand. Start studying dna replication labeling. It is thought that these flanking segments mediate the binding of mammalian dna ligases to other proteins involved in dna replication, repair, and recombination. They are joined together to produce a continuous daughter strand. Dna replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its dna.
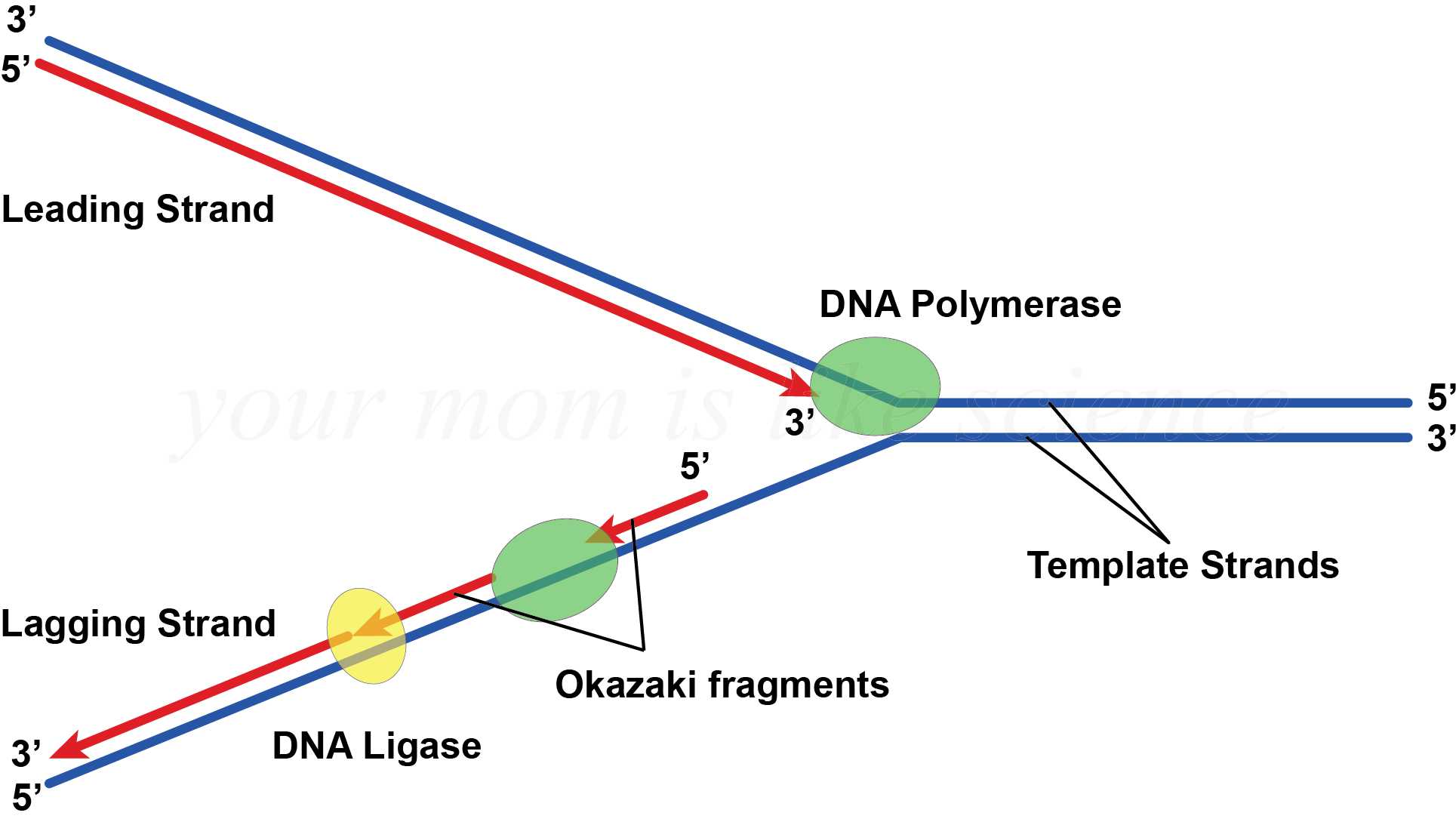
Start studying dna replication labeling. The majority of ligation reactions involve dna fragments that have been generated by restriction enzyme digestion. Dna replication — steps & diagram. Roles of dna polymerases and other replication enzymes. We know substantially more about dna synthesis in once replication has been initiated; Dna replication has been well studied in bacteria primarily because of the small size of the genome and the mutants that are available. They are joined together to produce a continuous daughter strand. An enzyme that connects two fragments of dna to make a single fragment. The rna primers are removed and replaced with dna nucleotides by bacterial dna polymerase i, and dna ligase seals the gaps between these fragments. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together. Short segment of dna synthesized discontinuously in small segments in the 3' to 5' direction by ligase. Dna ligase 4provided by hgnc. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or dna, like the parent cell.
They bind to the dna molecule at the origin sites, thus flagging it for the docking of other proteins and enzymes essential for dna replication. This leads to the formation of two. Roles of dna polymerases and other replication enzymes. Dna is the genetic material and is propagated throughout generations. Dna replication is fundamental process occurring in all living organism to copy their dna.
Dna replication — steps & diagram. Details of dna replication can be discussed under the following headings the dna double helix unwinds and uncoils into single strands of dna by breakdown of weak hydrogen bonds. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together. Dna replication begins at specific site termed as origin of replication, which has a specific sequence that can be recognized by initiator proteins called dnaa. The rna primers are removed and replaced with dna nucleotides by bacterial dna polymerase i, and dna ligase seals the gaps between these fragments. The lagging strand is therefore synthesised in fragments. The process is called replication in sense that each strand of ds dna serve as template for reproduction of complementary strand. Initiation of dna replication in microorganisms (e. Nitrogen bases of the nucleotides are ligase enzymes (not shown) connect sugars to phosphates along the newly created backbones. Dna replication is carried out by a complex system of enzymes. Therefore, dna replication requires that the dna is loosened and the double helix is unwound. Schematic diagram of dna replication. The fragments are then sealed together by an enzyme called ligase.
We know substantially more about dna synthesis in once replication has been initiated; ligase dna. A deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base.
Ligase Dna Replication Diagram: Short segment of dna synthesized discontinuously in small segments in the 3' to 5' direction by ligase.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar